Automation
The serverless CA can be deployed and updated using a CI/CD pipeline.
GitHub Actions example
For examples using GitHub Actions see one of the test GitHub Actions workflows within this repository, or the Cloud CA deployment workflow shown below:
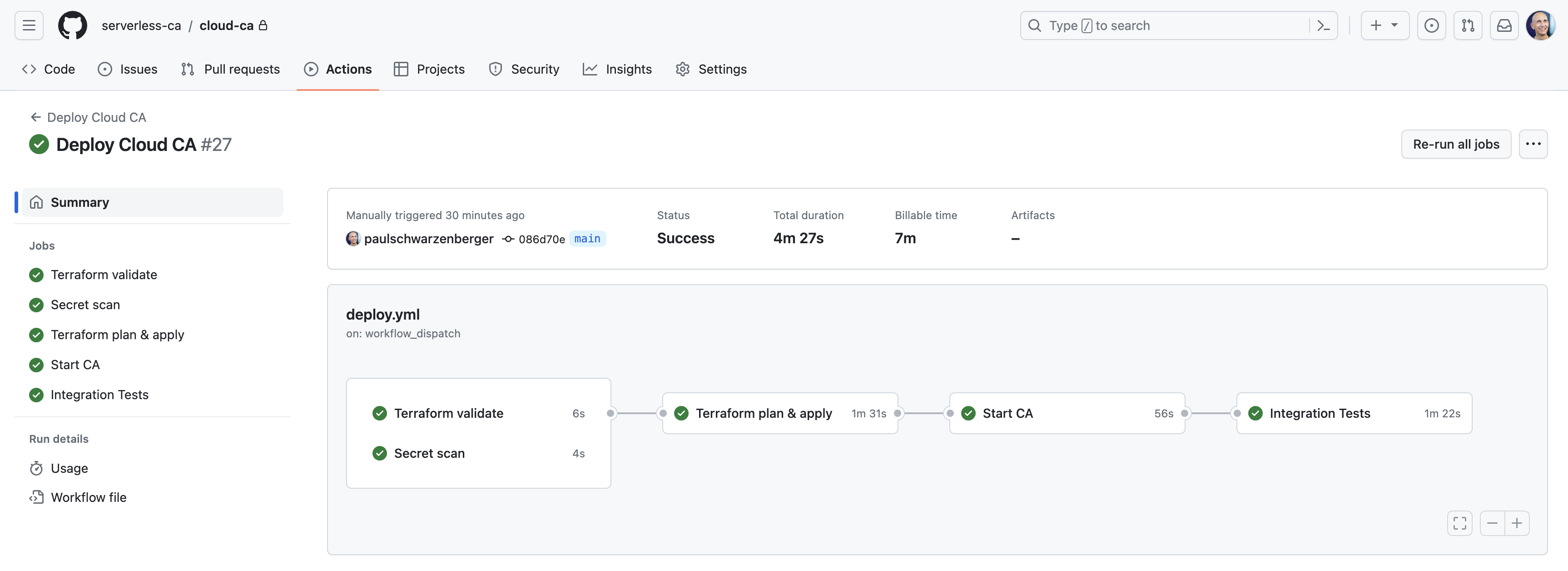
The principal steps are:
- Terraform validate
- Secret scan using GitLeaks
- Terraform plan
- Terraform apply
- Start CA
- Integration tests
Further details are provided below:
Caching Lambda zips
So that Lambda functions only get rebuilt when needed, the Lambda package zip files are cached and can be viewed in the GitHub Actions cache:
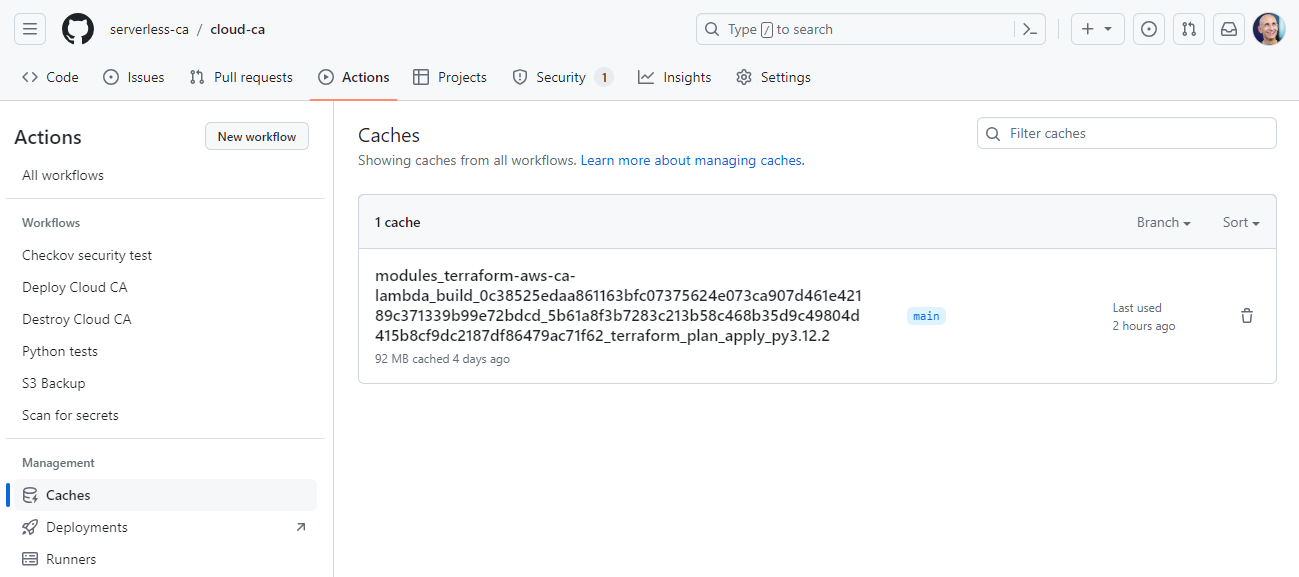
To ensure Lambda functions are updated when needed, check the cache name includes source code hashes and the Python version.
Approve Terraform apply
If you require a manual approval of Terraform Apply, use a GitHub Actions environment. Protect the environment with an Environment Protection rule requiring approval by an appropriate GitHub team.
Start CA
The Start CA job forces an immediate execution of the AWS Step Function. If this is omitted, the CA will only be created or updated on the next scheduled run which may take up to 24 hours.
Integration Tests
Integration tests include:
- certificate issued with no passphrase
- issued cert only includes client auth extension
- certificate issued with passphrase
- issued cert includes distinguished name specified in CSR
- issued cert includes correct DNS names in SAN
- issued cert with no SAN includes correct DNS name
- certificate issued without SAN if common name invalid
To reduce the risk of test certificates and keys being compromised and then used to access your environment, test certificates are:
- not saved to disk on the GitHub Actions runner
- short lifetime (1 day)
Issue Certificates using GitOps
Optionally, certificates can be issued using a GitOps process, as detailed in Client Certificates.
Certificate Revocation
Certificate revocation is via a GitOps process, as detailed in Revocation.